Aiolos’ load models use a technique called adaption. This means that the very latest load information received can be used to update the model formulation generated during the base data period (in the Aiolos model this period is one year back).
Adaption involves an adaptation of the load’s level. By producing a forecast with measured weather for the period most recently prior to the forecast period and comparing this with the actual result (outcome), Aiolos can estimate whether the level is different compared to that of the model.

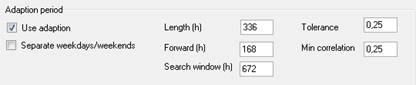
Here you can specify conditions for this level adjustment. “Length (h)” specifies the length of the test forecast period; “Forward” indicates how many hours of the forecast you want the correction to be applied to; “Tolerance” specifies the amount of deviation between test forecast and result (outcome) that can be allowed for in calculating the correction – i.e. if abs((forecast-outcome)/outcome) > tolerance, the value is not used.
“Search window (h)” indicates the maximum number of hours back in time from the forecast start that the adaption period is to be located.
“Min correlation” specifies a threshold value for the correlation between the corrected test forecast and the actual result (outcome). If the correlation is below this value, a warning message appears after the forecast has been produced.
The check box “Separate weekdays/weekends” indicates whether the system is to have a separate adaption for weekends and weekdays, respectively. Normally there is no advantage to be gained in this.
Here individual tests are recommended before conditions are imposed.